


Remember that the hole is removed from the shape, so its contribution to the total moment of inertia is negative. Organize all the necessary information into a table, then total the moments of inertia of the parts to get the moment of inertia of the whole shape. The moment of inertia depends on how mass is distributed around an axis of rotation, and will vary depending on the chosen axis.\(\require Solution The moment of inertia plays the role in rotational kinetics that mass (inertia) plays in linear kinetics-both characterize the resistance of a body to changes in its motion.
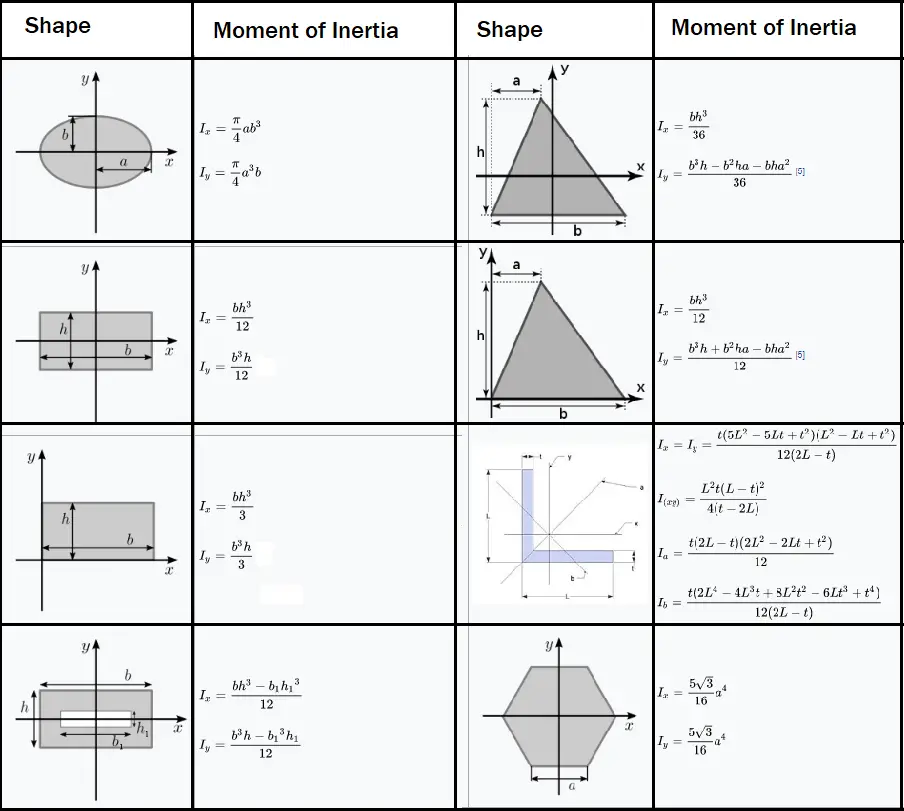
When a body is free to rotate around an axis, torque must be applied to change its angular momentum. 8 Inertia matrix in different reference frames.7.3 Derivation of the tensor components.7.2.1 Determine inertia convention (Principal axes method).6.5 Scalar moment of inertia in a plane.The formula and derivation can be found in this thread. For the polar moment of inertia, which is what you would use to calculate the force for a bolt group where a moment is about the centroid of the bolt group, is Ix + Iy. 6 Motion in space of a rigid body, and the inertia matrix The moment of inertia of the bolts themselves about their individual centroids is ignored as being inconsequential.For bodies free to rotate in three dimensions, their moments can be described by a symmetric 3 × 3 matrix, with a set of mutually perpendicular principal axes for which this matrix is diagonal and torques around the axes act independently of each other. Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis.įor bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane, a scalar value, matters. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of the point mass is defined to be the mass times the square of its rotation radius. To introduce the concept of moment of inertia, let us first look at a point mass m moving in a circle of radius r. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rate of rotation. Moment of inertia is the inertia of a rotating body with respect to its rotation. The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. War planes have lesser moment of inertia for maneuverability.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
